Learn how recruiters can detect AI Copilot usage in interviews by spotting behavioral patterns, delays, red flags, and inconsistencies in answers.

Abhishek Kaushik
Feb 3, 2026
AI copilots are rapidly becoming the invisible participant in online interviews. Candidates now rely on real time AI assistance to generate code, answer technical questions, and even guide behavioral responses while recruiters believe they are evaluating genuine skill.
This shift has created a new hiring risk. Recruiters are no longer just screening candidates. They are screening candidates plus AI. A recent Gartner survey reveals employers are increasingly concerned with identity fraud, as 6% of candidates admitted to fraudulent behavior during interviews, such as impersonation or using proxies. Gartner predicts this issue will escalate, estimating that by 2028, one in four candidate profiles worldwide will be falsified.
Recent hiring audits show a steep increase in candidates using AI assistance tools during live interviews, especially for technical and product roles. Many of these candidates perform exceptionally well in interviews but struggle immediately after joining.
The problem is not smarter candidates. The problem is hidden AI copilots.
This guide explains how recruiters can identify AI copilot usage, why traditional interview methods fail, and how Sherlock AI detects these signals in real time.
Red Flags: How to Spot an AI Copilot
AI assisted candidates rarely look suspicious at first glance. In fact, they often appear more confident and technically strong than genuine applicants. The key difference lies in behavioral inconsistencies that emerge during live questioning, coding, and problem solving. These patterns reflect AI response behavior rather than natural human thinking.
Here are the most reliable red flags recruiters should watch for.

1. Scanning Eye Movement
Candidates using AI often shift their gaze repeatedly toward a fixed direction where another device or screen is placed. This movement is subtle but consistent and usually happens before they begin answering.
Example: While explaining a coding solution, the candidate keeps glancing downward every few seconds as if reading text.
2. Processing Delay Followed by Perfect Answer
AI needs time to generate structured responses. Candidates pause unnaturally longer than normal thinking time and then provide highly polished answers without hesitation.
Example: You ask about system scalability. Candidate stays silent for 10 to 15 seconds and then delivers a textbook level structured explanation.
3. Echoing the Question
Repeating or paraphrasing the question allows time for the AI to produce an answer. This often sounds natural but becomes suspicious when used frequently.
Example:
Interviewer: "How would you handle API rate limiting?"
Candidate: "Rate limiting is an important mechanism used to control traffic…" (repeating to buy time).
4. Textbook Technical Language
AI responses sound formal and definition heavy. Candidates relying on AI use perfect theoretical phrasing rather than experiential or conversational explanations.
Example: Candidate explains cloud architecture like reading documentation instead of describing real implementation.
5. Sudden Skill Jump During Interview
At the beginning, AI lacks context. As the interview progresses, responses suddenly become sharper and more accurate once the tool adapts.
Example: Candidate struggles early with simple logic but later answers complex technical questions flawlessly.
6. Robotic Speech Pattern
AI generated text read aloud sounds unnaturally structured and monotone. Human answers typically include filler words, pauses, and conversational variation.
Example: Behavioral answers sound like scripted corporate training material.
7. Instant Code Pasting
Candidates stop typing, then suddenly insert large blocks of correct code. This indicates copying from an AI tool rather than writing live.
Example: Candidate types slowly for a minute and then pastes an entire working function instantly.
8. No Natural Debugging Process
Real developers test ideas and fix errors gradually. AI assisted candidates often pause silently and replace the code entirely.
Example: Instead of troubleshooting errors, candidate waits and pastes a corrected solution.
9. Screen Attention Mismatch
Candidate claims to be thinking but is not actively interacting with the screen. Their attention is likely on another AI device.
Example: Cursor remains idle while candidate looks away frequently.
Correct Answers Without Personal Depth
AI provides generic correctness but lacks project specific detail. Candidates cannot explain real life scenarios behind their answers.
Example: Candidate perfectly explains caching but fails to describe where they used it.
Perfect Syntax Under Pressure
Humans make small mistakes during live coding. AI generated code is unusually clean and error free even in complex logic.
Example: Candidate writes advanced recursion flawlessly without corrections.
Delayed Clarification Questions
AI often suggests clarifying questions after generating partial answers. This results in candidates asking important constraints late.
Example: Candidate asks "What are the input limits?" only after a long pause.
13. Audio Echo or Hidden Assistant Noise
AI voice copilots running nearby create faint echoes or delayed playback artifacts that can sometimes be heard.
Example: A slight echo follows the interviewer’s speech or soft background whispering is detected.
When several of these signals appear together, it strongly suggests AI copilot usage rather than genuine expertise.
Why Recruiters Cannot Reliably Detect AI Copilots Manually
Even experienced recruiters struggle to confirm AI usage with certainty. Most signals are behavioral and subtle. Candidates appear polished, confident, and technically correct, which makes suspicion difficult to act on without proof.
Manual detection fails because:
Recruiters only see answers, not the candidate’s environment
AI assistance happens off screen on secondary devices
Behavioral clues are easy to miss in fast paced interviews
Interviewers hesitate to accuse without evidence
Skilled candidates hide AI usage naturally
This creates a dangerous hiring gap where AI supported candidates outperform genuinely skilled ones.
Recruiters need more than observation. They need measurable proof.
How Sherlock AI Detects AI Copilot Usage in Real Time
Sherlock AI is designed to surface behaviors and patterns that indicate external AI assistance, interview fraud, or reasoning inconsistencies during live interviews. It combines multiple signal types into a unified detection model rather than relying on single superficial cues.
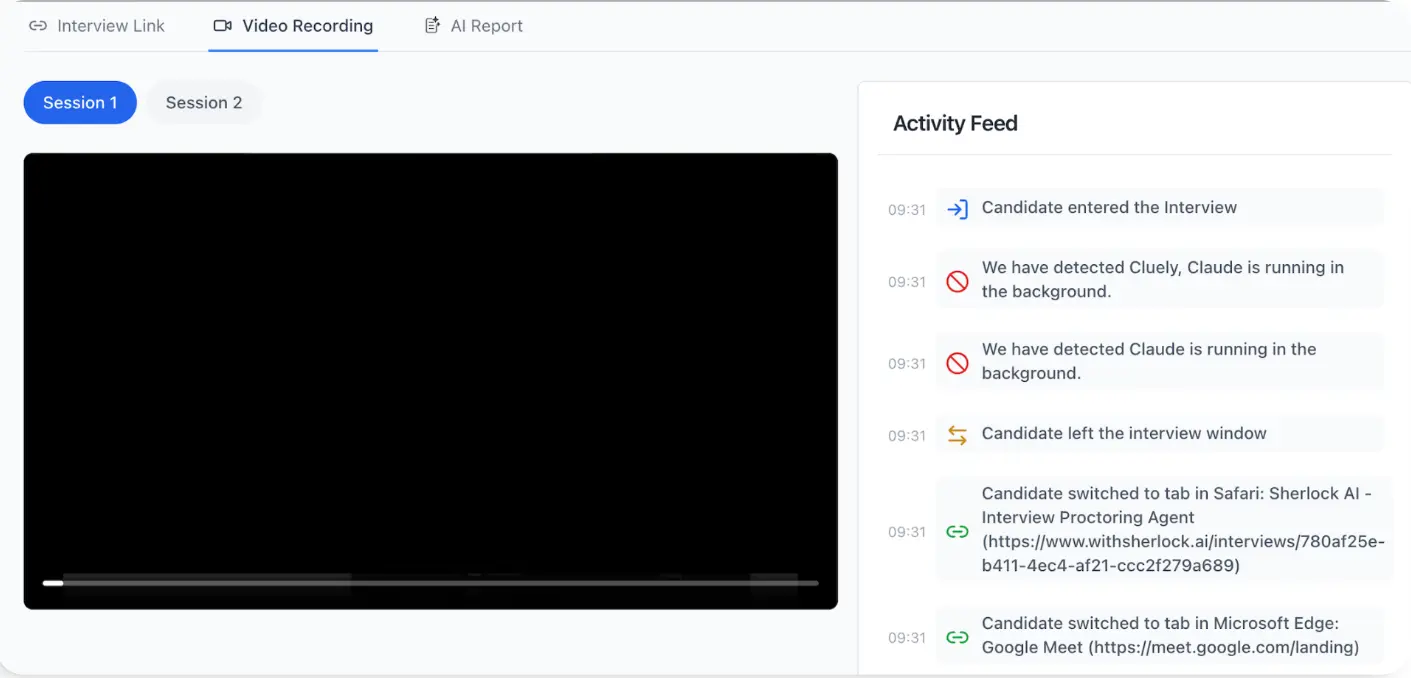
Key features:
Sherlock AI detects AI assisted behavior in interviews in real time.
It analyzes multiple behavioral and technical signals together.
It monitors candidate interaction patterns during live interviews.
It verifies identity continuity throughout the session.
It flags suspicious background audio or overlapping voices.
It detects hidden apps or secondary device activity.
It identifies abnormal typing and copy paste behavior.
It generates post interview integrity reports for recruiters.
It automatically integrates with calendars and joins meetings.
It evaluates AI fluency when controlled AI use is allowed.
It is built with a privacy first and non intrusive design.
Read More: How to Detect and Prevent Cluely AI in Interviews
The Future of Hiring Requires Authenticity Verification
AI copilots will only become more advanced and harder to notice. Traditional interviews alone cannot protect hiring decisions anymore.
Recruiters must adopt systems that verify human performance during interviews.
Sherlock AI acts as the silent verification layer that protects organizations from AI assisted fraud and ensures every hire reflects genuine skill.

Final Thoughts
AI copilots have fundamentally changed the dynamics of remote interviews. What once relied on human preparation and real time thinking can now be artificially enhanced with invisible AI support. This makes interview performance an unreliable indicator of actual skill unless recruiters can verify authenticity.
The challenge is no longer identifying whether candidates know the answer. It is determining whether they arrived at that answer independently. Behavioral inconsistencies, delayed perfection, and copied code are all signals that traditional interview processes were never designed to detect.
Sherlock AI fills this critical gap. By monitoring live behavioral patterns, device activity, identity continuity, and interaction authenticity, it gives recruiters something they have never had before in remote hiring: objective proof of real human performance.
In the AI driven hiring era, accuracy will not come from better questions. It will come from better verification.



