Explore best tools to detect plagiarism & identify AI-generated, copied, and coached answers in coding and technical interviews.

Abhishek Kaushik
Nov 26, 2025
Technical interviews in 2026 increasingly include:
AI-assisted coding
Copied system design templates
Coached project narratives
Proxy interviewers interacting on behalf of candidates
Traditional interview methods were not designed to detect this. But new detection tools can surface authenticity signals in real time.
Tools to Detect Plagiarism in Technical Interviews
We review the leading approach and compare it to older manual methods still used today.
1. Sherlock AI (AI Interview Integrity Layer)
Sherlock AI is purpose-built to detect fraud, impersonation, and AI-coached responses in live interviews conducted on Zoom, Teams, Meet, or browser-based coding environments.
What Sherlock AI Detects Automatically
Detection Area | Signals Collected | Example Indicators |
|---|---|---|
Identity Integrity | Face match, voice match, camera continuity | Candidate swaps, proxy involvement |
Thought Authenticity | Live reasoning vs scripted answer patterns | Memorized vs real experience answers |
Code Ownership | Typing cadence, editing style, problem solving narration | Copied code vs constructed code |
External Assistance | Hidden prompts, second screens, remote control attempts | Copy-paste anomalies |
Why This Works
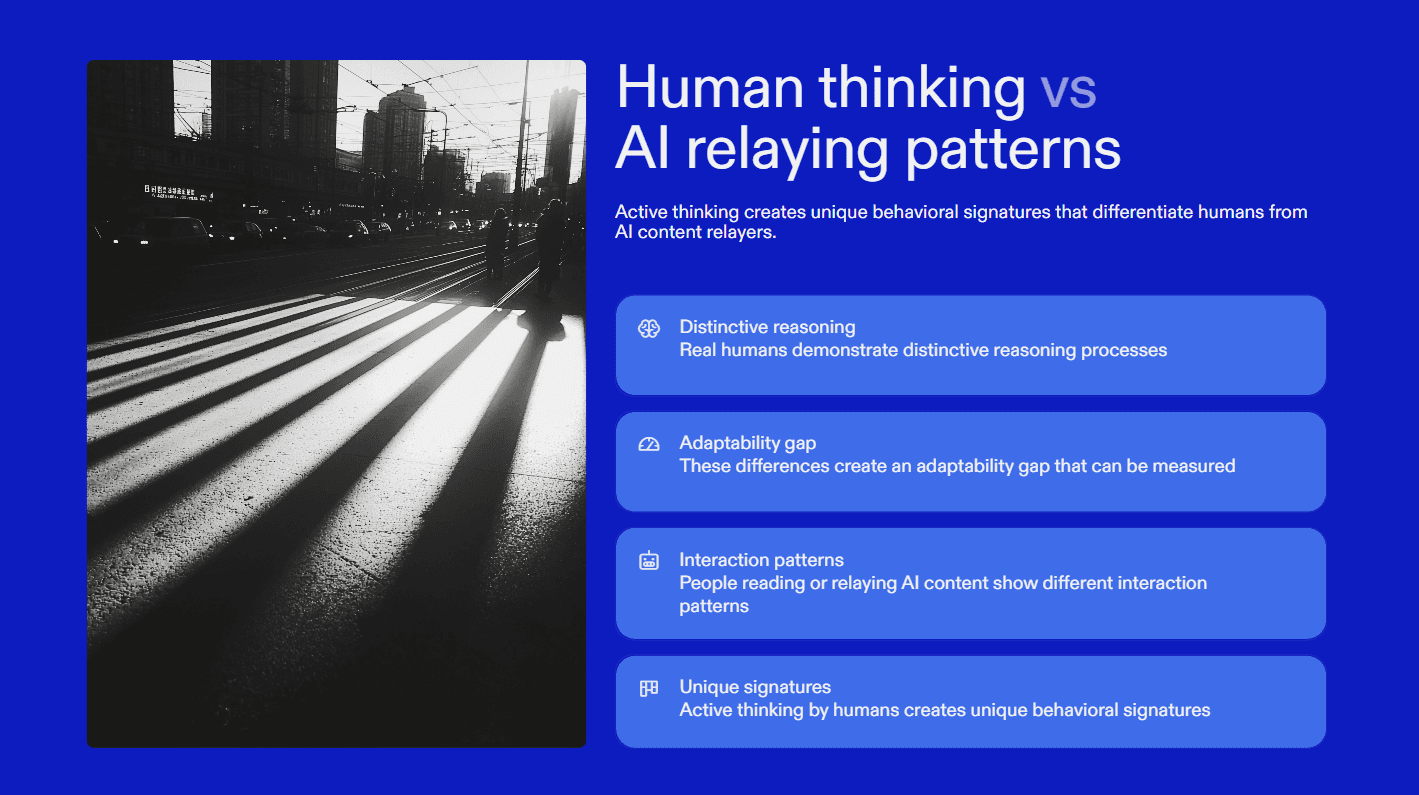
Sherlock AI does not try to guess intent. It detects behavioral and reasoning patterns that differ between:
A person actively thinking
A person reading or relaying generated answers
In a multi-company dataset across 14 roles, candidates who could not adapt reasoning when constraints changed were 7 times more likely to have used coached or AI-assisted answers.
Sherlock AI exposes that adaptability gap in real time.
2. Manual Screen Recording Review
Still common in many companies.
Pros
Useful when detecting obvious fraud
Can be used during audit review
Cons
Time consuming
Reviewer bias risk
Misses subtle coaching
Only works after the interview is already over
Manual review is reactive, not preventive.
3. Plagiarism Checkers for Code
Typical tools:
GitHub Copilot Output Detection
MOSS (Measure of Software Similarity)
Codequiry
JPlag
What They Detect
Structural similarities in code
Common template reuse
Shared logic flow patterns
Limitations
They require final code, so they cannot detect help during the interview
They do not evaluate reasoning or decision-making depth
They miss coached verbal explanations entirely
Code plagiarism detection helps with output authenticity, not thinking authenticity.
4. Live Pair Programming Observation
Interviewers watch:
How candidates break down problems
Where they pause
How they adjust if stuck
This is effective, but only when interviewers are trained to ask:
What alternative approaches did you consider
What changed while solving
What tradeoffs influenced your decision
Untrained interviewers mistake fluency for competence.
5. Behavioral Cross-Checking
Verification technique:
Ask:
What changed in the project after the first release?
Ask again later in the interview in different words.
Authentic candidates:
Answer consistently
Provide detail tied to real constraints
Coached candidates:
Repeat surface-level phrases
Produce generic improvement narratives
Cannot anchor the story to actual technical tradeoffs
This reveals experience ownership, not memorized storytelling.
6. Constraint Shift Test (High Signal)
This is the single most effective manual method.
After the candidate explains a system or code approach, ask:
If your assumption about traffic, latency, or data shape changed, what would have to be redesigned?
Real engineers update their solution clearly. AI-generated or coached answers collapse when conditions change.
This is the core reasoning integrity check.
Summary Comparison
Method | Detects Live Fraud | Detects AI Coaching | Detects Copied Code | Detects Experience Ownership | Effort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sherlock AI | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Automated |
Screen Review | Sometimes | No | No | Weak | High |
Code Plagiarism Tools | No | No | Yes | No | Medium |
Pair Programming | Yes (with training) | Sometimes | Yes | Yes | High |
Behavioral Cross-Check | No | Yes | No | Yes | Medium |
Constraint Shift | No | Yes | No | Yes | Low |
Conclusion
Detecting plagiarism in technical interviews is not about:
Spotting suspicious facial expressions
Asking harder questions
Lengthening interview loops
It is about evaluating how the candidate thinks when the situation changes.
Tools like Sherlock AI surface this automatically. Traditional methods require interviewer training and more time.
To scale fairly and reliably, companies benefit from combining:
Real-time detection
Reasoning-based interviewing
Clear documentation standards
This reduces:
Hiring risk
Performance failures in the first 90 days
Legal and audit concerns



