Learn how to detect AI voice bots in interviews using red flags, live verification techniques, and real-time detection with Sherlock AI.

Abhishek Kaushik
Feb 5, 2026
Artificial intelligence is transforming the hiring landscape but not all of its impacts are positive. It’s also fueling a rise in AI-generated interview fraud, including deepfake voice bots that impersonate real people in remote interviews. Recent research shows that 17 percent of hiring managers have encountered candidates using AI deepfakes to alter video or audio interviews.
The broader risk is escalating fast: industry analysts predict that by 2028, as many as one in four job candidates worldwide could be fake, driven largely by generative AI tools that make synthetic voices and likenesses shockingly easy to produce. Meanwhile, fraud statistics across sectors show that deepfake and synthetic voice attacks have surged more than 1,300 percent in recent years, underlining how rapidly AI misuse is outpacing detection capabilities.
With these trends converging, employers face a new reality - AI voice bots aren’t just theoretical threats, they’re active and growing risks in remote interviews.
What AI Voice Bots Are and How They Work
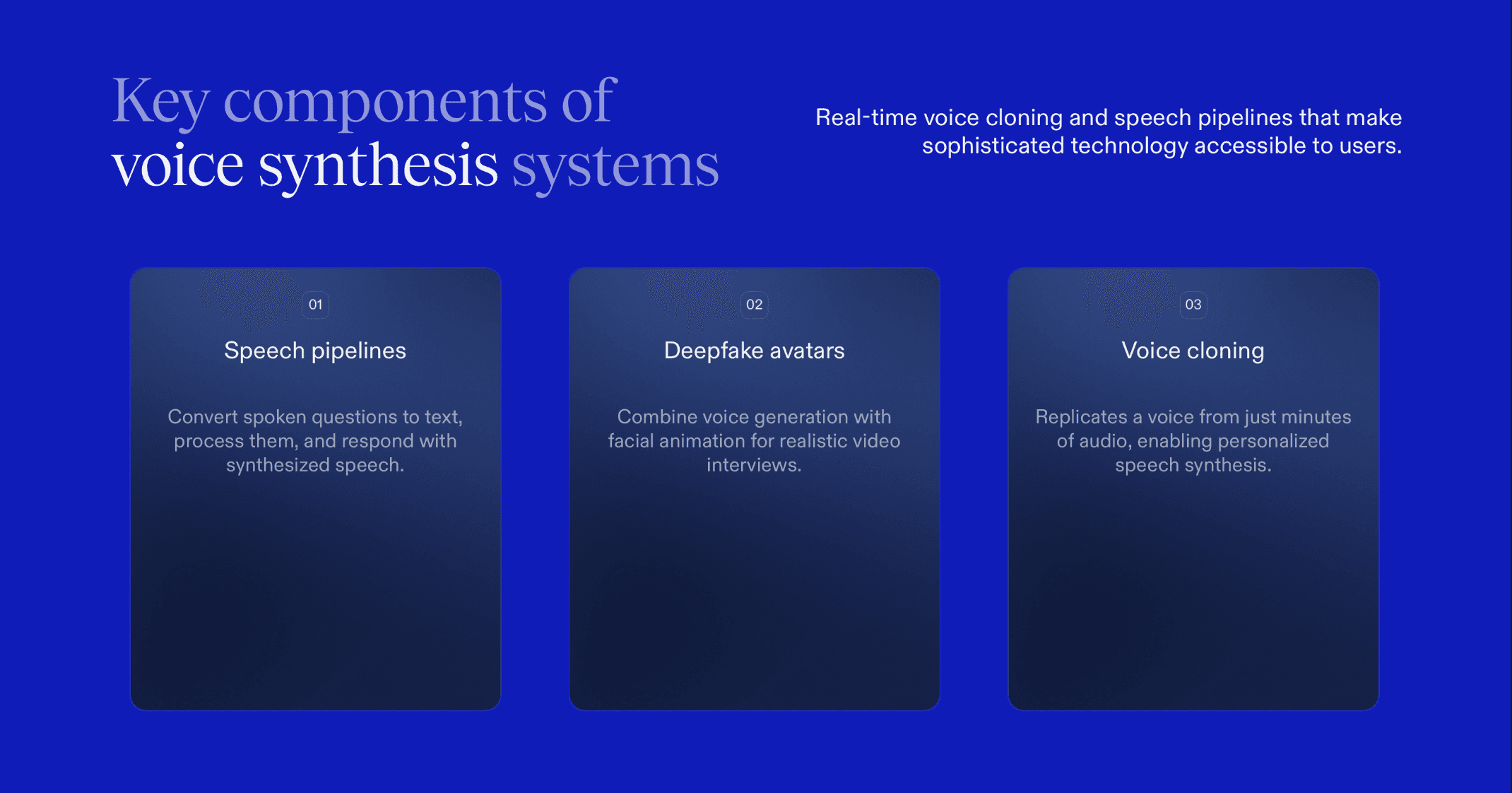
AI voice bots and synthetic speech technologies use advanced machine learning models to replicate human voices and generate natural-sounding audio. These systems can include:
Real-time voice cloning: AI analyzes a few minutes (or sometimes just seconds) of audio and then generates new speech in that voice, matching tone, accent, and rhythm. These tools require minimal technical skills and increasingly appear in widely accessible platforms.
Speech-to-speech and TTS pipelines: A spoken question is transcribed to text (speech-to-text), passed to an LLM to generate a response, and then converted back to audio using text-to-speech (TTS) models, effectively creating a real-time AI interviewer or interviewee.
Deepfake avatars: Some systems integrate voice generation with facial animation and lip-syncing, making the fake speaker appear even more convincing in a video interview.
What used to be specialized research tech is now accessible to average users, making sophisticated misuse easier than ever.
Common Cheating Scenarios
Here are the major ways AI voice tech is being abused in interview contexts:
1. Candidates using AI to generate spoken answers live
Rather than answering questions themselves, candidates can use AI assistants running behind the scenes (via voice or hidden software) to craft perfect answers with speech output sounding natural and confident.
These setups can hide behind natural delays and subtle pauses, making detection harder.
2. Proxy interviews powered by voice cloning
In more extreme cases, a deepfake voice and video avatar can be used so that someone other than the real candidate appears to interview.
This means an impostor could theoretically pass as the applicant in multiple remote screens.
3. AI assisting non-native speakers
Some candidates may use AI translation plus speech generation to sound fluent in languages they don’t actually speak, turning the interview into a simultaneous AI-mediated performance.
While translation tools are intended to help, in hiring contexts this can blur the line between assistance and deception.
Behavioral and Technical Red Flags That Indicate an AI Voice Bot
As AI voice technologies become more advanced, detecting them purely by ear can be challenging but there are consistent patterns, inconsistencies, and subtle cues that often betray synthetic or AI-assisted speech. Below are the key voice-related, interaction, and behavioral red flags every recruiter should watch for plus simple real-time tactics to verify authenticity.

1. Voice-Related Red Flags
AI voice bots and text-to-speech models, even the advanced ones, still differ from human speech in predictable ways:
Perfect fluency with unnatural pacing or intonation
Human speakers naturally vary pacing, rhythm, emphasis, and prosody. AI voices may sound too smooth, too consistent, or mechanically balanced lacking the small, natural hesitations people exhibit when thinking.
Answers may sound “too polished” across questions of varying difficulty.
No filler words, pauses, or self-corrections
Most humans use filler words like “um,” “uh,” “you know,” or pause briefly to think.
AI systems typically generate full sentences with no hesitation or self-correction, which can be a red flag when responses are long or complex.
Identical tone and energy across all answers
Emotional tone naturally shifts with topic, comfort level, and difficulty.
AI systems often maintain a flat or uniform emotional profile, even when the subject matter would normally trigger excitement, concern, or hesitation.
Slight audio artifacts or robotic resonance
Even high-quality TTS models may have tiny glitches like short pops, unnatural decay on consonants, or a “synthetic” timbre.
These artifacts may be subtle but become more noticeable during long answers or rapid back-and-forth.
2. Interaction Red Flags
Behavioral responses can be just as telling as audio quality:
Delays before complex answers
Human thinking produces varying response times, especially for difficult or technical questions.
AI systems may have a consistent delay pattern (e.g., always same pause before every answer), or longer pauses only on more complex prompts, indicating backend processing.
Failure to interrupt naturally or react emotionally
Humans interrupt awkwardly or adjust mid-sentence; AI may finish every sentence too formally, without timing interruptions the way a person would.
Emotional reactions (surprise, humour, confusion) may be missing or delayed.
Inconsistent pronunciation of the same words
A speaker pronouncing the same uncommon word differently in different parts of the same interview can be suspicious, particularly if pronunciation shifts with question phrasing.
These inconsistencies may arise in AI systems using hybrid models or chaining text-to-speech pipelines.
3. Behavioral Inconsistencies
AI voice detection isn’t just about voice quality, it’s also about how speech syncs with human behavior:
Voice confidence not matching facial expressions or body language
In video interviews, mismatches between vocal confidence and visual cues (e.g., uncertain body language while sounding flawless) can be telling.
Similarly, if eye contact or facial reactions don’t align with emotional content in answers, double-check authenticity.
Sudden changes in accent or speaking style mid-interview
People’s accents and speech habits remain consistent within a reasonable range.
Sudden shifts, beyond minor natural variability, can signal stitched-together AI responses or switching between models.
Simple Live Verification Techniques
These quick techniques often throw AI systems off:
1. Ask the candidate to read a random sentence
It should be a sentence you generate on the spot, ideally with unusual words or complex punctuation.
AI may sound too-perfect, or repeatedly the same voice characteristics whereas a real person will show natural variation.
2. Ask them to describe something in their room
Human descriptions of real, immediate surroundings include sensory details, spontaneous phrasing, and short self-corrections.
AI-generated descriptions may lack specificity or have static phrasing.
3. Interrupt mid-answer and change the question
Real humans instinctively pivot or adjust language when the question changes mid-stream.
AI systems may complete the original prompt before addressing the pivot, or respond robotically.
Pro tip: Combine multiple techniques. No single red flag confirms an AI but patterns across voice, interaction, and behavior raise strong suspicion.
Sherlock AI: Real-Time Detection of AI Voice Bots in Interviews
Sherlock AI acts as a dedicated interview-integrity layer designed to detect synthetic voices, proxy speakers, and AI-assisted answering as they happen.
Rather than relying on surface-level audio quality checks, Sherlock AI analyzes deep behavioral and acoustic signals that indicate whether a real human is actually speaking.
How Sherlock AI Detects AI Voice Bots
Sherlock AI uses a multi-layered detection approach that combines audio forensics, behavioral analysis, and real-time monitoring:
• Voice authenticity analysis
Detects synthetic speech patterns common in text-to-speech and voice-cloning models.
Flags unnatural prosody, over-smooth intonation, robotic resonance, and spectral artifacts.
Identifies inconsistencies in vocal identity across different answers in the same interview.
• Latency and response-generation monitoring
Measures micro-delays between question delivery and answer onset.
Flags response timing patterns that match AI inference + TTS pipelines.
Detects suspicious consistency in answer start-times regardless of question difficulty.
• Speech-pattern and prosody modeling
Analyzes pacing, rhythm, emotional variation, and hesitation patterns.
Flags “too-perfect” fluency with no filler words or self-corrections.
Detects flat emotional tone across all answers.
• Voice fingerprint consistency checks
Builds a dynamic voice profile of the speaker across the interview.
Flags sudden changes in accent, pitch range, or vocal texture.
Detects stitched or switched synthetic voices.
Sherlock AI gives recruiters a forensic-level advantage, detecting synthetic speech, proxy speakers, and AI-assisted answers in real time, before fake candidates slip into your hiring funnel.
Conclusion
In a world where anyone can sound like anyone, trust in hiring can no longer be assumed, it must be verified.
Sherlock AI gives hiring teams a real-time defense against synthetic voices, proxy speakers, and AI-assisted answering. By continuously analyzing vocal authenticity, response timing, speech patterns, and behavioral consistency, it surfaces risks that human ears simply can’t detect and does so during the interview, when action can still be taken.
Organizations that adapt now by combining smarter interview design with real-time AI fraud detection will protect their hiring quality, reduce costly mis-hires, and stay ahead of a rapidly evolving threat landscape.



